Simon Boccanegra
Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa | Su |
Melodramma in a prologue and three acts
Libretto by Francesco Maria Piave
Music Giuseppe Verdi
Synopsis
Time: The middle of the 14th century.
Place: In and around Genoa.
Prologue
(Act 1 in the 1857 original)
A piazza in front of the Fieschi palace
Paolo Albiani, a plebeian, tells his ally Pietro that in the forthcoming election of the Doge, his choice for the plebeian candidate is Simon Boccanegra. Boccanegra arrives and is persuaded to stand when Paolo hints that if Boccanegra becomes Doge, the aristocratic Jacopo Fiesco will surely allow him to wed his daughter Maria. When Boccanegra has gone, Paolo gossips about Boccanegra's love affair with Maria Fiesco – Boccanegra and Maria have had a child, and the furious Fiesco has locked his daughter away in his palace. Pietro rallies a crowd of citizens to support Boccanegra. After the crowd has dispersed, Fiesco comes out of his palace, stricken with grief; Maria has just died (Il lacerato spirito – "The tortured soul of a sad father"). He swears vengeance on Boccanegra for destroying his family. When he meets Boccanegra he does not inform him of Maria's death. Boccanegra offers reconciliation and Fiesco promises clemency only if Boccanegra lets him have his granddaughter. Boccanegra explains he cannot because the child, put in the care of a nurse, has vanished. He enters the palace and finds the body of his beloved just before crowds pour in, hailing him as the new Doge.
Act 1
(Act 2 in the 1857 original)
[Twenty-five years have passed. Historically the action has moved from 1339, the year of Simon's election in the prologue, forward to 1363, the year of the historical Simone Boccanegra's death – for acts 1, 2 and 3.]
[The Doge has exiled many of his political opponents and confiscated their property. Among them is Jacopo Fiesco, who has been living in the Grimaldi palace, using the name Andrea Grimaldi to avoid discovery and plotting with Boccanegra's enemies to overthrow the Doge. The Grimaldis have adopted an orphaned child of unknown parentage after discovering her in a convent (she is in fact Boccanegra's child, Maria – known as Amelia – named after her mother, and she is Fiesco's granddaughter). They called her Amelia, hoping that she would be the heir to their family's fortune, their sons having been exiled and their own baby daughter having died. Amelia is now a young woman.]
Scene 1: A garden in the Grimaldi palace, before sunrise
Amelia is awaiting her lover, Gabriele Adorno (Aria:Come in quest'ora bruna – "How in the morning light / The sea and stars shine brightly"). She suspects him of plotting against the Doge and when he arrives she warns him of the dangers of political conspiracy. Word arrives that the Doge is coming. Amelia, fearing that the Doge will force her to marry Paolo, now his councilor, urges Adorno to ask her guardian Andrea (in reality, Fiesco) for permission for them to marry: Sì, sì dell'ara il giubilo / contrasti il fato avverso – "Yes, let the joy of marriage be set against unkind fate".
[1857 original version: the duet ended with a cabaletta (set to the same words as the 1881 text) then "a coda and a battery of chords followed by applause."]
Fiesco reveals to Adorno that Amelia is not a Grimaldi, but a foundling adopted by the family. When Adorno says that he does not care, Fiesco blesses the marriage. Boccanegra enters and tells Amelia that he has pardoned her exiled brothers. She tells him that she is in love, but not with Paolo, whom she refuses to marry. Boccanegra has no desire to force Amelia into a marriage against her will. She tells him that she was adopted and that she has one souvenir of her mother, a picture in a locket. The two compare Amelia's picture with Boccanegra's, and Boccanegra realizes that she is his long-lost daughter. Finally reunited, they are overcome with joy. Amelia goes into the palace. Soon after, Paolo arrives to find out if Amelia has accepted him. Boccanegra tells him that the marriage will not take place. Furious, Paolo arranges for Amelia to be kidnapped.
Scene 2: The council chamber
[1881 revision: This entire scene was added by Verdi and Boito in place of the 1857 scene, which took place in a large square in Genoa.] [29][30]
The Doge encourages his councillors to make peace with Venice. He is interrupted by the sounds of a mob calling for blood. Paolo suspects that his kidnapping plot has failed. The Doge prevents anyone leaving the council chamber and orders the doors to be thrown open. A crowd bursts in, chasing Adorno. Adorno confesses to killing Lorenzino, a plebeian, who had kidnapped Amelia, claiming to have done so at the order of a high-ranking official. Adorno incorrectly guesses the official was Boccanegra and is about to attack him when Amelia rushes in and stops him (Aria: Nell'ora soave – "At that sweet hour which invites ecstasy / I was walking alone by the sea"). She describes her abduction and escape. Before she is able to identify her kidnapper, fighting breaks out once more. Boccanegra establishes order and has Adorno arrested for the night (Aria: Plebe! Patrizi! Popolo! – "Plebeians! Patricians! Inheritors / Of a fierce history"). He orders the crowd to make peace and they praise his mercy. Realizing that Paolo is responsible for the kidnapping, Boccanegra places him in charge of finding the culprit. He then makes everyone, including Paolo, utter a curse on the kidnapper.
Act 2
(Act 3 in the 1857 original)
The Doge's apartments
[1881 revised version: There are some small adjustments in this act which include expanding Paolo's opening aria, thus giving him greater stature in the work: Me stesso ho maledetto! / "I have cursed myself", the wording of which was originally: O doge ingrato ... ch'io rinunci Amelia e i suoi tesori? / "O ungrateful Doge! ... Must I give up Amelia and her charms".] [31]
Paolo has imprisoned Fiesco. Determined to kill Boccanegra, Paolo pours a slow-acting poison into the Doge's water, and then tries to convince Fiesco to murder Boccanegra in return for his freedom. Fiesco refuses. Paolo next suggests to Adorno that Amelia is the Doge's mistress, hoping Adorno will murder Boccanegra in a jealous rage. Adorno is furious (Aria: Sento avvampar nell'anima – "I feel a furious jealousy / Setting my soul on fire"). Amelia enters the Doge's apartments, seeming to confirm Adorno's suspicions, and he angrily accuses her of infidelity. She claims only to love him, but cannot reveal her secret – that Boccanegra is her father – because Adorno's family were killed by the Doge. Adorno hides as Boccanegra is heard approaching. Amelia confesses to Boccanegra that she is in love with his enemy Adorno. Boccanegra is angry, but tells his daughter that if the young nobleman changes his ways, he may pardon him. He asks Amelia to leave, and then takes a drink of the poisoned water, which Paolo has placed on the table. He falls asleep. Adorno emerges and is about to kill Boccanegra, when Amelia returns in time to stop him. Boccanegra wakes and reveals to Adorno that Amelia is his daughter. Adorno begs for Amelia's forgiveness (Trio: Perdon, Amelia ... Indomito – "Forgive me, Amelia ... A wild, / Jealous love was mine"). Noises of fighting are heard – Paolo has stirred up a revolution against the Doge. Adorno promises to fight for Boccanegra, who vows that Adorno shall marry Amelia if he can crush the rebels.
Act 3
(Act 4 in the 1857 original)
[1857 original version: Act 4 opened with a double male voice chorus, and a confused dialogue involving references to details in the original play.][32]
Inside the Doge's palace
The uprising against the Doge has been put down. Paolo has been condemned to death for fighting with the rebels against the Doge. Fiesco is released from prison by the Doge's men. On his way to the scaffold, Paolo boasts to Fiesco that he has poisoned Boccanegra. Fiesco is deeply shocked. He confronts Boccanegra, who is now dying from Paolo's poison. Boccanegra recognizes his old enemy and tells Fiesco that Amelia is his granddaughter. Fiesco feels great remorse and tells Boccanegra about the poison. Adorno and Amelia, newly married, arrive to find the two men reconciled. Boccanegra tells Amelia that Fiesco is her grandfather and, before he dies, names Adorno his successor. The crowd mourns the death of the Doge.
Program and cast
Conductor: Michele Mariotti
Director: Richard Jones
Maestro del Coro: Ciro Visco
Set and costume designer: Antony McDonald
Lighting designer: Adam Silverman
CAST
Simon Boccanegra Luca Salsi / Claudio Sgura 29 Nov, 1, 4 Dec
Maria Boccanegra (Amelia) Eleonora Buratto/ Maria Motolygina 29 Nov, 1, 4 Dec
Jacopo Fiesco Michele Pertusi / Dmitri Ulyanov 29 Nov, 1, 4 Dec
Gabriele Adorno Stefan Pop/ Antony Ciaramitaro 29 Nov, 1, 4 Dec
Paolo Albiani Gevorg Hakobyan
Pietro Luciano Leoni
Teatro dell’Opera di Roma Orchestra and Chorus
A Teatro dell’Opera di Roma new production
Teatro dell'Opera di Roma - Teatro Costanzi
A new way to discover the finest details in different opera houses, theatres one can explore from home in advance through the revolutionary GOOGLE PERFORMING ARTS PROJECT. CLICK ON THE LINK TO SEE THE THEATER.
The Teatro dell'Opera, from its building (1879), at Domenico Costanzi’s request (1810-1898), and 1926, when it was bought by the then Governor of RomE, bore the name of Domenico Costanzi, building contractor and impresario, who committed the building to the Milanese architect Achille Sfondrini (1836-1900), specialized in theatre building and renovation. Built in 18 months on the area prevIously occupied by Heliogabalus’ villa, it was inaugurated on November 27th, 1880 with Semiramide by G. Rossini, conducted by the Maestro Giovanni Rossi, in the presence of the King and Queen of Italy.
Sfrondini’s design privileges the acoustic effect, by conceiving the interior structure as a "resonance chamber": as is particularly evident from the horseshoe shape. At the beginning, the theatre, with a seating capacity of 2,212 spectators, had three tiers of boxes, an amphitheatre, a gallery. All was surmounted by a dome with splendid frescoes by Annibale Brugnoli.
Costanzi invested all his personal assets in the venture. However, due to the despotic refusal of the City Council to redeem the theatre, Costanzi was obliged to manage it himself. Despite the fact that he had to deal with huge financial problems, under his management the opera house held many world premières of such operas as Cavalleria Rusticana (on May 17th, 1890) and L'Amico Fritz(October 31st 1891), both by Pietro Mascagni, who then became very well known.
For a brief period, the theatre was managed by the founder's son, Enrico Costanzi, who contributed to other great premières: Tosca by Giacomo Puccini (January 14th, 1900) and Le Maschere (January 17th, 1901). In 1907, the Teatro Costanzi was managed by the impresario Walter Mocchi (1870-1955) on behalf of the Società Teatrale Internazionale e Nazionale (STIN).
In 1912 Emma Carelli (1877-1928), Mocchi's wife, became the managing director of the new «Impresa Costanzi», named as such following various changes in the company structure. With Rome City Council’s purchase of Costanzi company, the theatre became “Teatro Reale dell'Opera” and a partial rebuilding was commissioned to the architect Marcello Piacentini. Closed on November 15th, 1926, it was re-opened on February 27th, 1928 with the opera Nerone by Arrigo Boito, conducted by the Maestro Gino Marinuzzi.
With the advent of the Republic, the theatre gained the current name of Teatro dell'Opera. In 1958, the building was further remodeled and modernised at the request of the Rome City Council. In over a century, the Teatro dell’Opera has seen its prestige increase internationally. During the several seasons, the most acclaimed voices worldwide followed one another: Enrico Caruso; Beniamino Gigli; Aureliano Pertile; Giacomo Lauri-Volpi; Claudia Muzio; Maria Caniglia; Maria Callas; Renata Tebaldi; Montserrat Caballé; Marilyn Horne; Raina Kabaivanska; Mario Del Monaco; Franco Corelli; Giuseppe Di Stefano; Tito Gobbi; Alfredo Kraus; Ruggero Raimondi; José Carreras; Placido Domingo and Luciano Pavarotti. Among the finest conductors, we can mention Otto Klemperer, Arturo Toscanini, Victor De Sabata, Marinuzzi,Vittorio Gui, Tullio Serafin, Von Karajan, Gianandrea Gavazzeni, Carlo Maria Giulini, Georg Solti, Claudio Abbado, Georges Prêtre, Zubin Mehta, Lorin Maazel, Mstislav Rostropovich, Giuseppe Patanè, Giuseppe Sinopoli, Wolfgang Sawallisch, Nino Sanzogno, Gianluigi Gelmetti and since 2008 the Maestro Riccardo Muti.
How to reach Teatro dell'Opera
Piazza Beniamino Gigli, 7
METRO
Linea A - REPUBBLICA TEATRO DELL'OPERA stop
BUS
Via Nazionale - H, 40, 60, 64, 70, 71, 170, 116T
Via Depretis - 70, 71
Via Cavour - 16, 75, 84, 150 (festivo), 360, 590, 649, 714
Stazione Termini - 16, 38, 75, 86, 90, 217, 310, 360, 649, 714
TAXI
phone number - 06.3570

 EN
EN DE
DE IT
IT FR
FR ES
ES RU
RU JP
JP RO
RO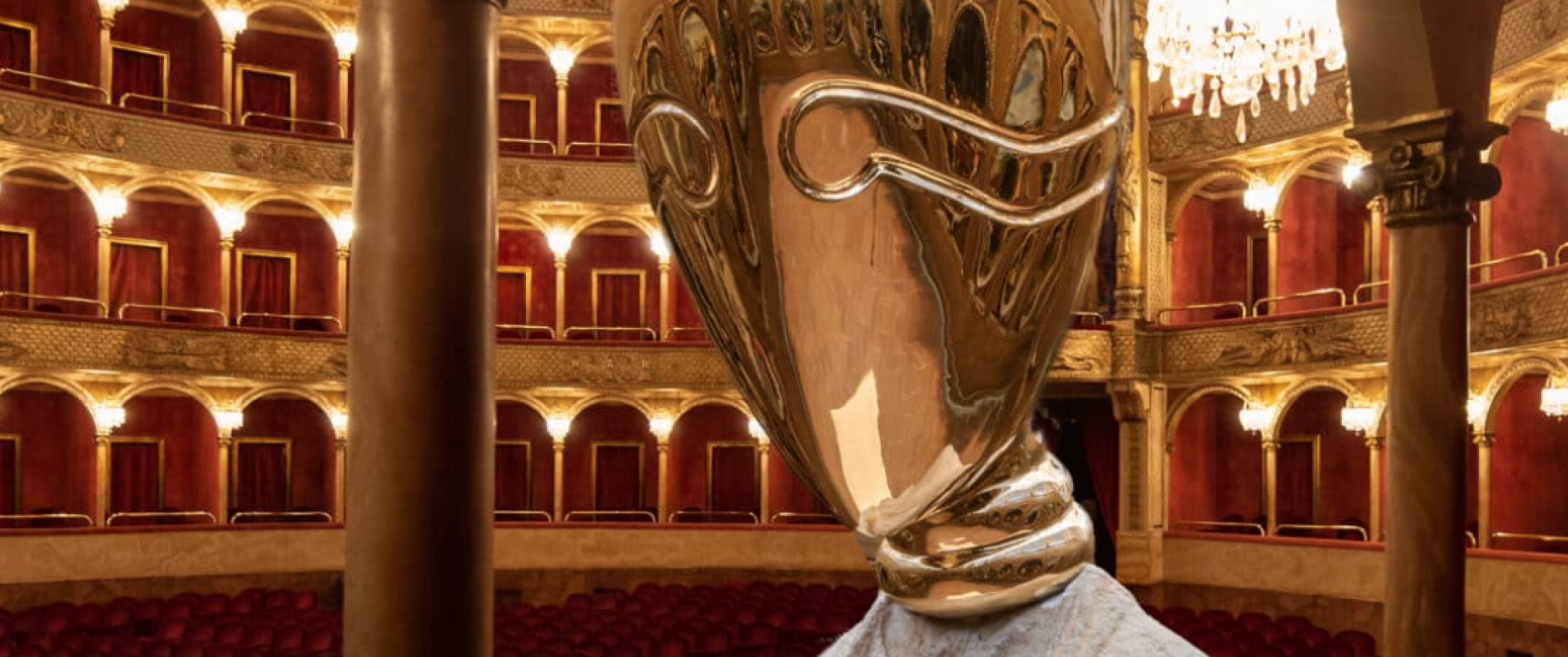
 Seating plan
Seating plan